Endocrine System Introduction

Overview
In this lesson, we introduce the anatomy (structure) and physiology (functions and relationships) of the endocrine system, also called the hormonal or glandular system.
Objective
Gain an understanding of the anatomy and physiology of the endocrine (glandular or hormonal) system.
What You'll Get
Describe the endocrine system and define glands and hormones. Explain how the endocrine system and nervous system are similar and how they are different. Describe the hypothalamus, its location and the hormones it secretes. Explain the different ways in which various resources refer to the hypothalamus and its role in the endocrine system. List the primary endocrine glands from the head downward and describe the primary functions of each.
Vocabulary
adrenal glands, endocrine system, glands, gonads, hormones, hypothalamus, pancreas, parathyroid, pineal gland, pituitary gland, thymus, thyroid

- ADRENAL GLANDS — Two small, triangular-shaped endocrine glands that release hormones including cortisol and adrenaline, impacting a range of functions including heart rate, blood pressure, immunity and managing physical stress responses
- DUCTLESS GLANDS — Organs whose secretions are deposited directly into the blood, not to tubes or ducts
- ENDOCRINE SYSTEM — Comprised of glands which release hormones into the bloodstream, “telling” the body how to function or grow
- GLANDS — Organs that secrete something such as saliva, sweat, breast milk or hormones
- GONADS — Reproductive or “sex glands”
- HORMONES — Natural, complex chemicals that modify cells and affect many different functions, including respiration, metabolism, reproduction, sensory perception, movement, sexual development and growth
- HYPOTHALAMUS — A part of the brain that links the nervous system and the endocrine system; serves as the control center for autonomic, endocrine, and motor function; secretes hormones including vasopressin, oxytocin and growth hormone
- MELATONIN — A hormone produced from serotonin and secreted by the pineal gland in response to darkness; therapeutic for various diseases and sleep disorders
- PANCREAS — Both a digestive organ (producing enzymes that serve digestion) and an endocrine organ (secreting insulin and glucagon which help to regulate glucose levels in the blood)
- PARATHYROID — An endocrine gland associated with the amount of calcium in the body
- PINEAL GLAND — Small, pine-cone shaped gland located near the center of the brain; secretes melatonin; associated with the third-eye
- PITUITARY GLAND — Pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain, makes hormones that trigger growth
- THYMUS — An endocrine gland with a primary role in immunity
- THYROID — A butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the neck; associated with growth, energy, calorie-burning and heart rate
Anatomy & Physiology Introduction
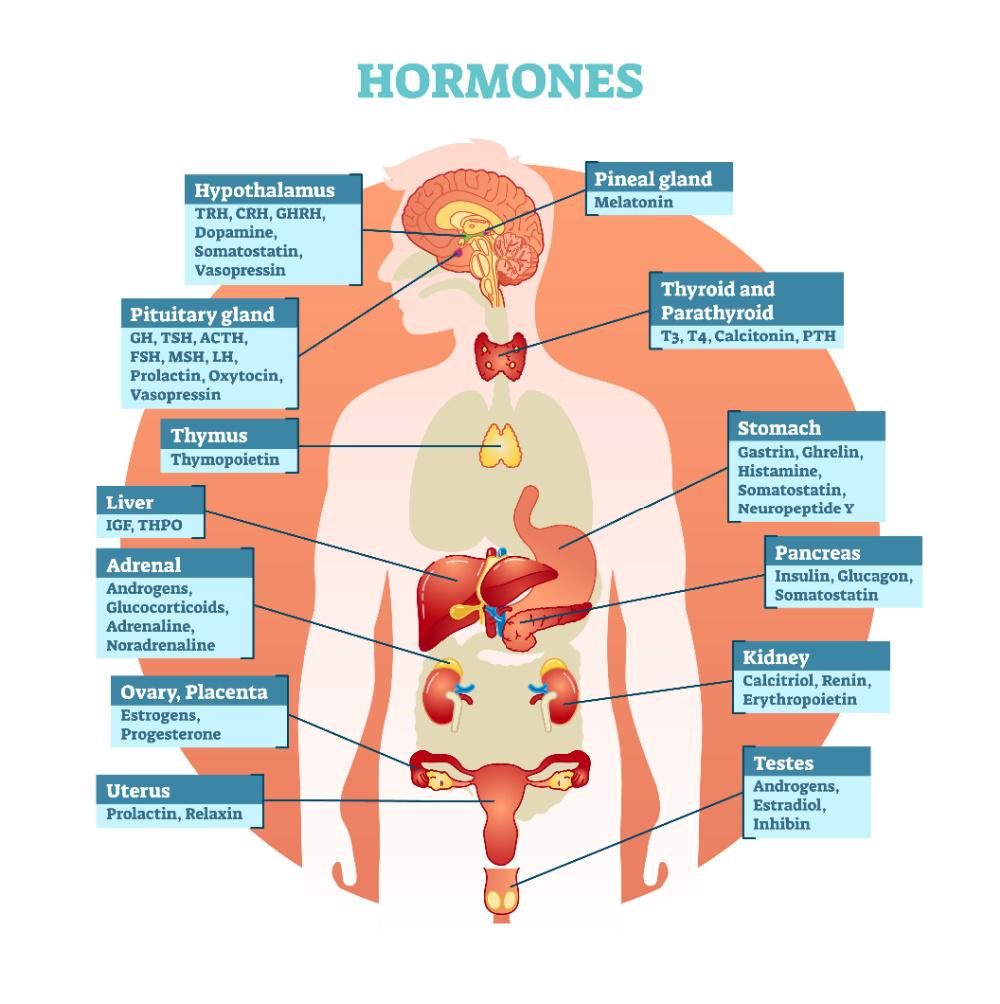
A “gland” is the name given to organs that secrete something such as saliva, sweat, breast milk or hormones
Endocrine glands are also known as the ductless glands because of the fact that their secretions are released directly into the blood, not to any tubes or ducts. (source)
The endocrine system is comprised of glands which release hormones into the bloodstream.
- Hormones are chemicals that regulate bodily processes by sending signals to “tell” the body how to function or grow. (source) “Hormones are complex chemical structures that, by modifying the activities of particular cells that respond to them, eventually modify the body’s tissues and organs as well.” (Gary Kraftsow)
- Hormones relate to many different functions, including respiration, metabolism, reproduction, sensory perception, movement, sexual development and growth.
The hypothalamus is a part of the brain that links the endocrine system and the nervous system. Both the nervous system and endocrine system are responsible for communication between organs and tissues, helping to regulate many bodily activities. While the nervous system communicates via neurons, the endocrine system uses hormones which travel through the circulatory system.
VARYING CONCENTRATIONS OF HORMONES IN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
Unlike the nervous system where signals occur only in preexisting nerve tracts, the endocrine system’s hormonal signals can travel expansively throughout the circulatory system with relatively continuous yet varying effect depending upon the concentration of hormones (rather than being purely on/off). – Mark Stephens
Endocrine System & The Brain
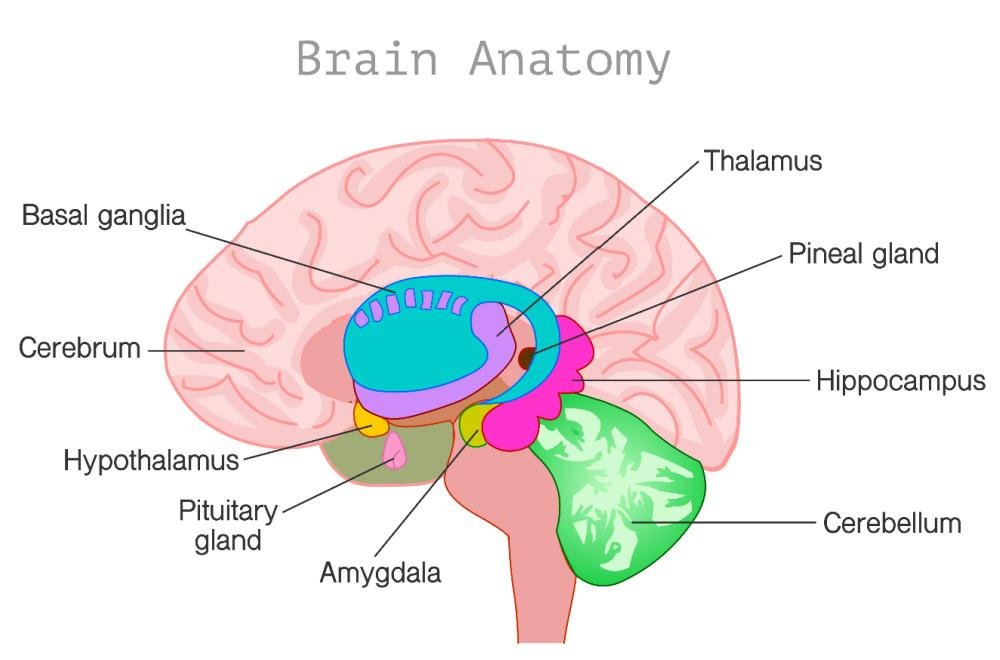
The endocrine system and the brain are intimately linked.
They share organs.
And they are in a feedback loop, with hormones as the messengers:
- Within the brain are the hypothalamus, pineal and pituitary glands — part of the endocrine system.
- Hormones are important messengers both within the brain and between the brain and the body. (brainfacts.org)
- The endocrine system and the brain are in a feedback loop, flowing from the brain to the pituitary gland to an endocrine gland and back to the brain.
Continue Reading with Ashtanga Tech
This study guide is available to members. Join to access 800+ in-depth guides on anatomy, philosophy, sequencing, and the science of practice.
Join for $5.50/mo — the cost of a DC coffeeAlready a member? Log in here

