Pineal Gland
Physical Characteristics
The pineal gland is very small, about the size of a grain of rice and shaped like a pine cone.
It’s located near the center of the brain.
The brain is comprised of two distinct hemispheres connected by fibers. The pineal gland is located in the middle of the brain, in between the two hemispheres. – Gage Gorman
Although located in the brain, the pineal gland is uniquely isolated from the blood-brain barrier system, so that it can secrete hormones into the blood. As a result, it’s vulnerable to toxins, including fluoride.
Independent discoveries have found the pineal to “possess all the essential features of the external eyes.” (source)
It contains rods and cones to process light… even though it’s smack dab in the center of our “dark” brains. – Christina Sarich
OUTSIDE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER,
THUS, VULNERABLE TO TOXINS INCLUDING FLUORIDE
Due to its location outside of the blood-brain barrier — a necessary phenomenon since it secretes hormones into blood circulation — it has little protection against exposure to toxins such as fluoride, making it prone to mineralization. – GreenMedInfo Research, More Fluoride Exposure Leads to Less Sleep
RESEARCH STUDY CONFIRMS FLUORIDE ACCUMULATES IN THE PINEAL GLAND
Fluoride deposits accumulate in the pineal gland and calcify it. “This study has added new knowledge on the fate and distribution of fluoride in the body. It has shown for the first time that fluoride readily accumulates in the human pineal gland.” – Jennifer Luke
PINEAL GLAND CALCIFICATION ASSOCIATED WITH SEVERAL CONDITIONS
This gland has one of the highest rates of calcification of all tissues in our bodies (7). Pineal gland calcification (PCG) is a hardening of the pineal gland’s tissue that is associated with several conditions, including Alzheimer’s, migraines, sleep disorders, and pediatric brain tumors. – Lacey Gibson
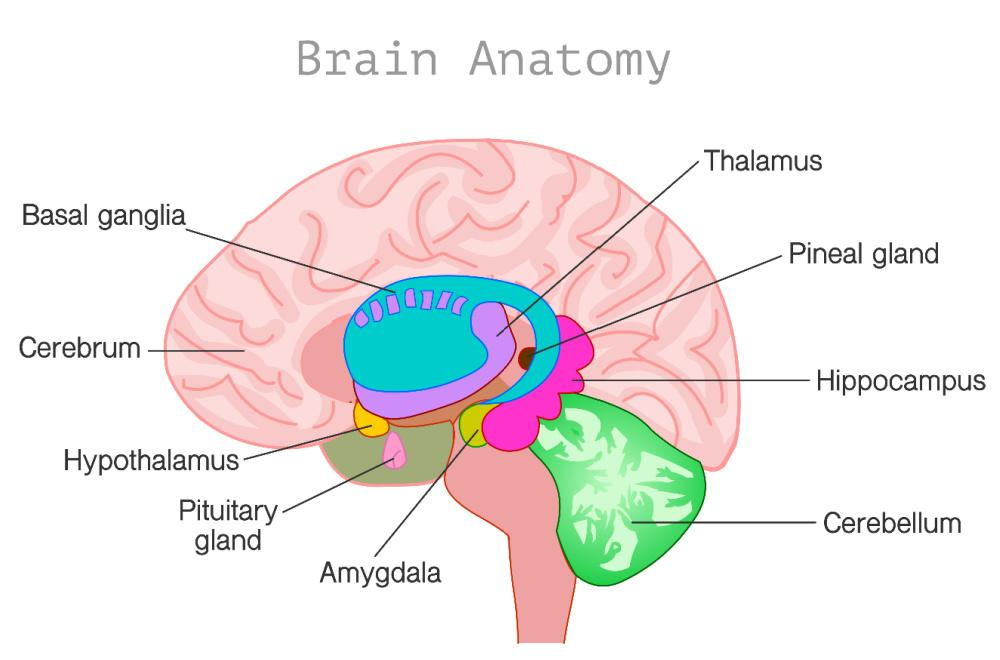
LOCATION USING MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
[It] lies within the roof of the third ventricle, deep within the brain… The ventricles are fluid-filled spaces, and the third ventricle extends from the large lateral ventricles to the narrow cerebral aqueduct, passing between the two halves of the part of the brain called the diencephalon. It is located within an area called the epithalamus, just behind the thalamus and above the cerebellum, resting at the back of the brain, near the brain stem. There is a small fluid-filled pineal recess that projects into the stalk of the pineal body, allowing for the hormones it produces to more easily be diffused throughout the brain. – Brandon Peters MD
PRECISELY LOCATED?
[The pineal gland] is situated in the exact position of the Divine Proportion of the Golden Mean (.618 the distance on a line drawn from the front of the brain to the rear, and from the top of the skull to the bottom), behind and slightly above the level of the Pituitary Gland. – Anthony Palomo
Physiology & Melatonin
Continue Reading with Ashtanga Tech
This study guide is available to members. Join to access 800+ in-depth guides on anatomy, philosophy, sequencing, and the science of practice.
Join for $5.50/mo — the cost of a DC coffeeAlready a member? Log in here

