Systems & Muscles Quiz
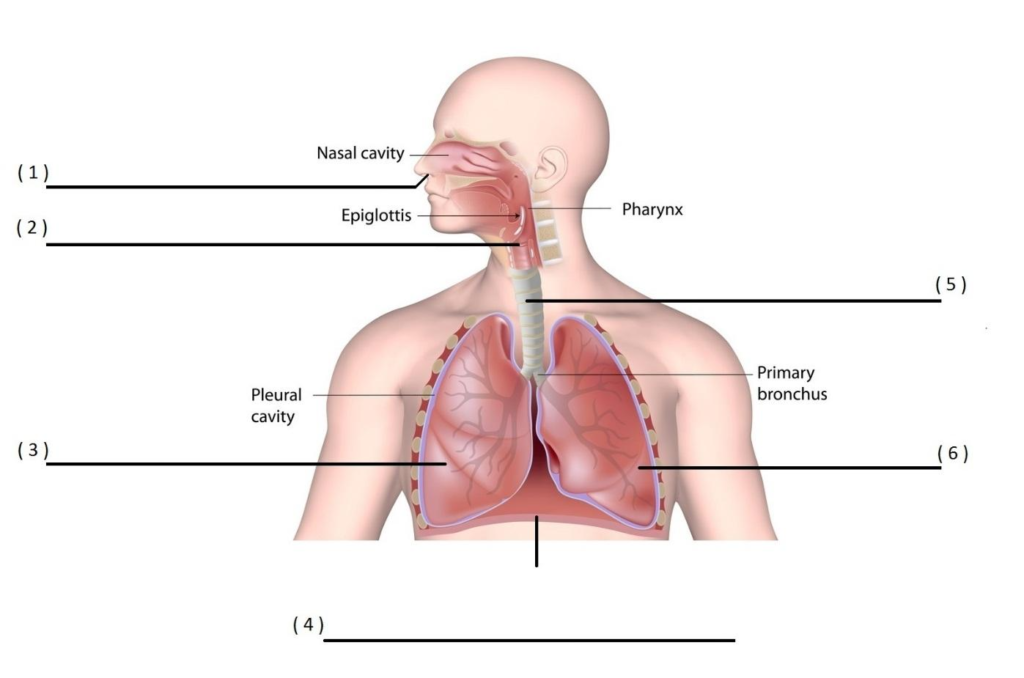
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
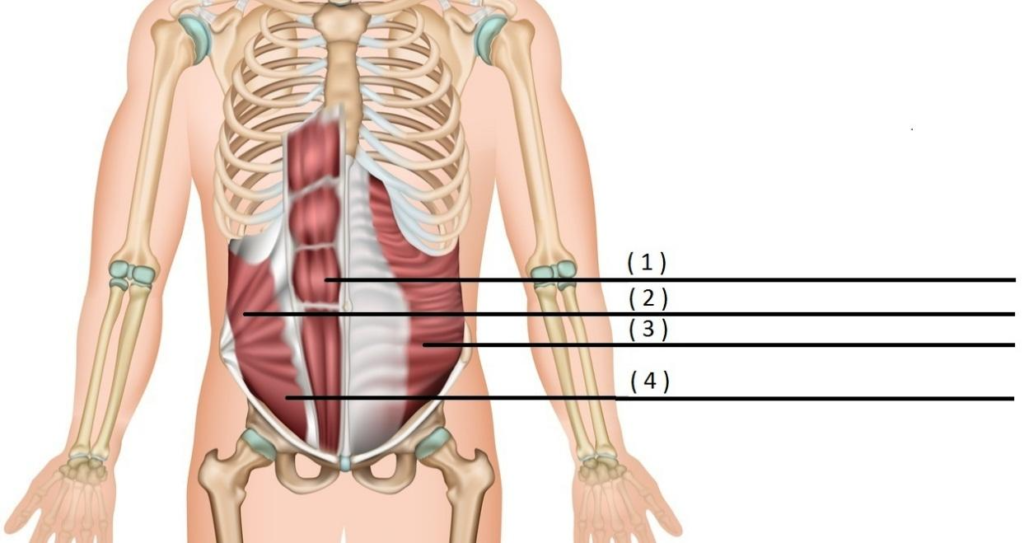
ABDOMINALS
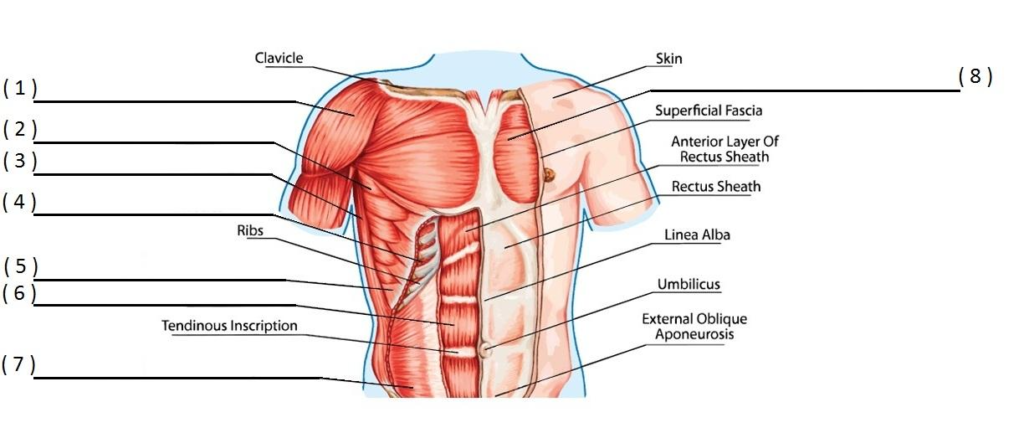
UPPER BODY MUSCLES
SHOULDER & ARM
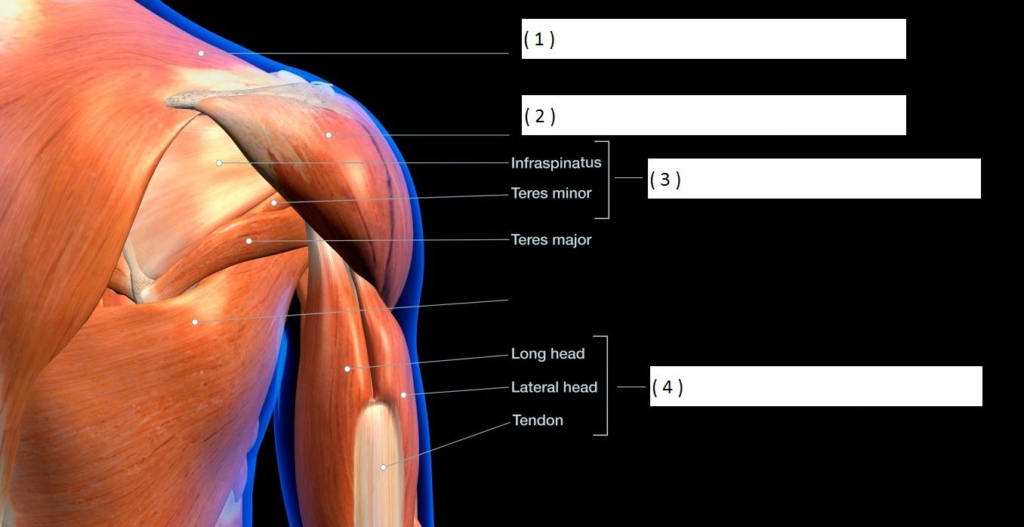
SHOULDER: DELTOIDS
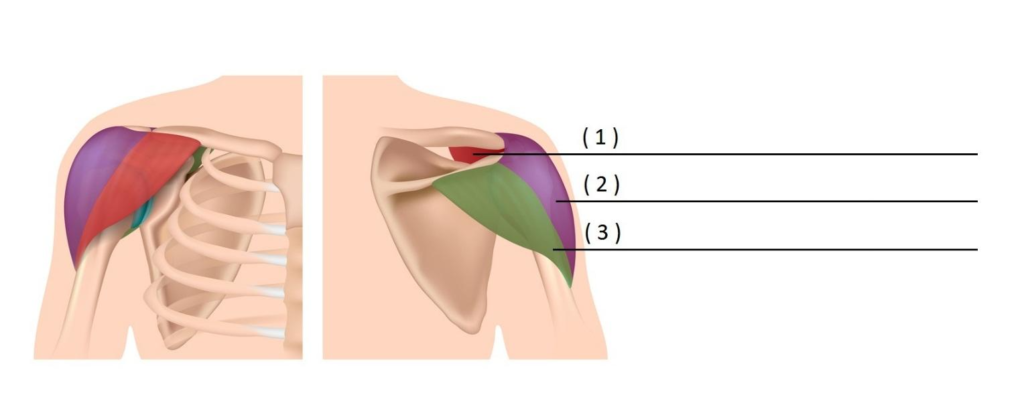
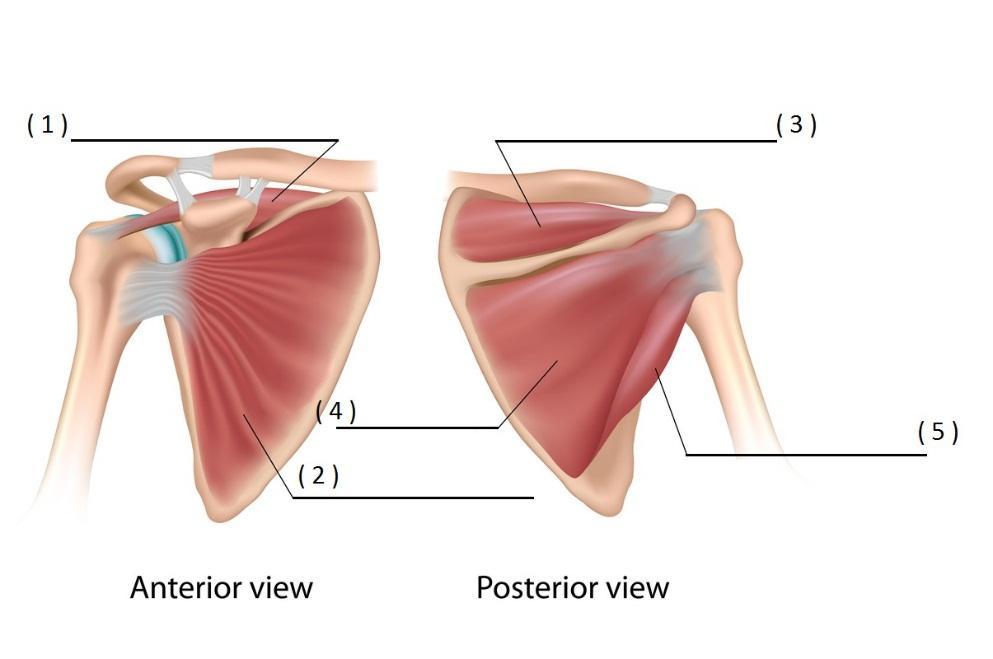
ROTATOR CUFF
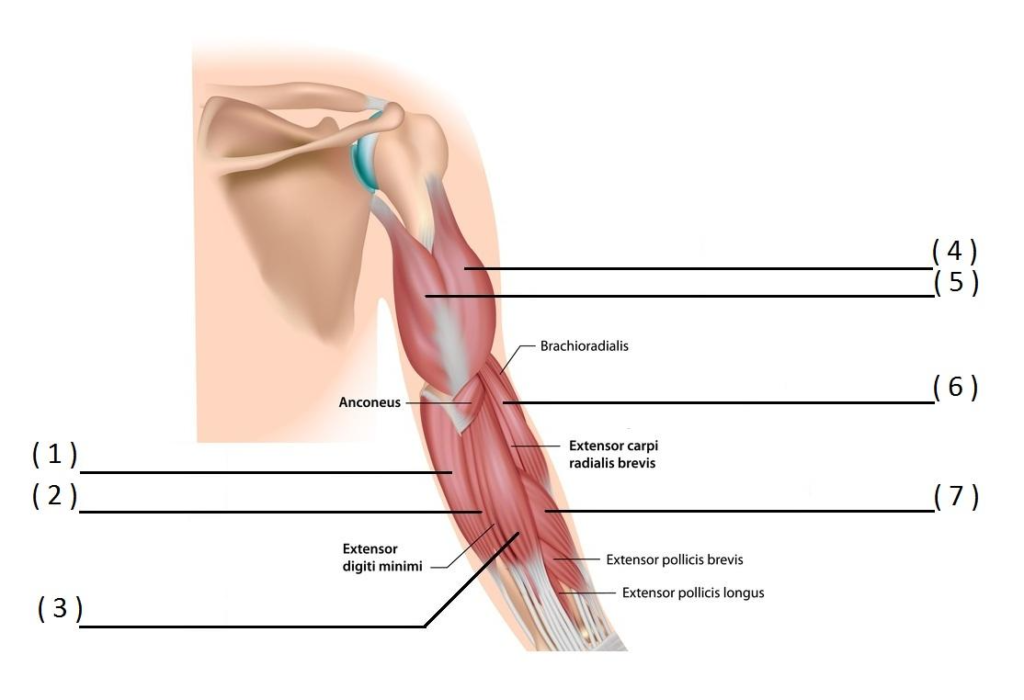
ARM
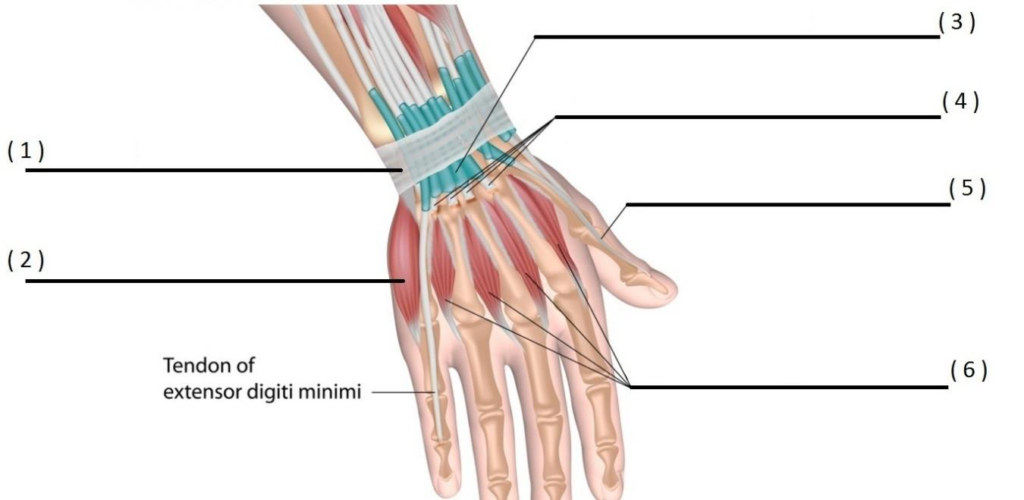
WRIST & HAND
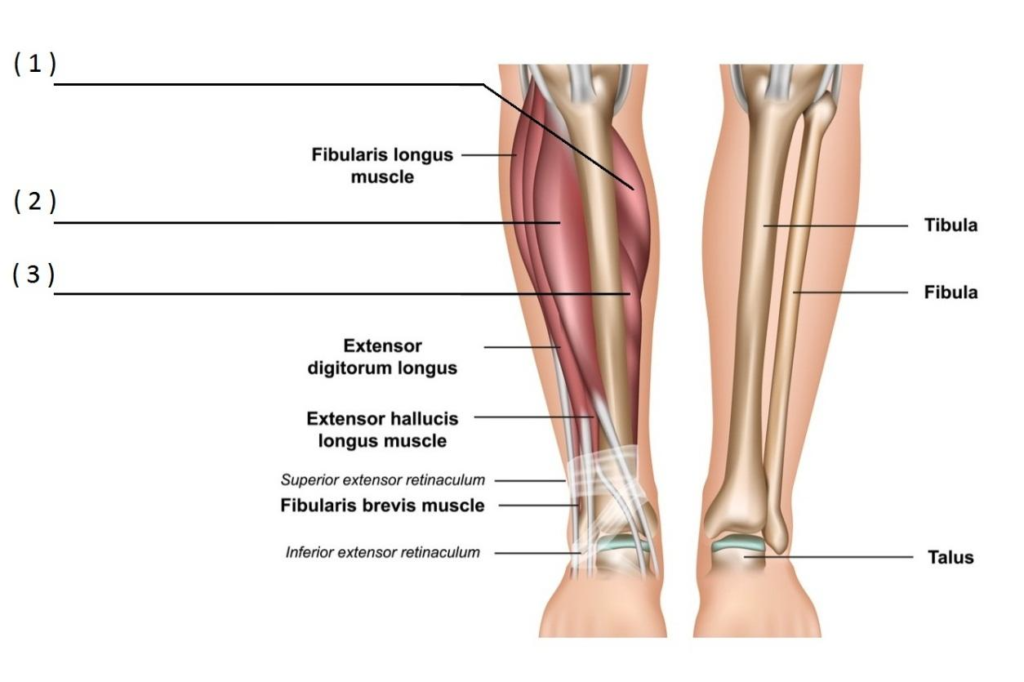
LOWER LEG MUSCLES
HIP JOINT
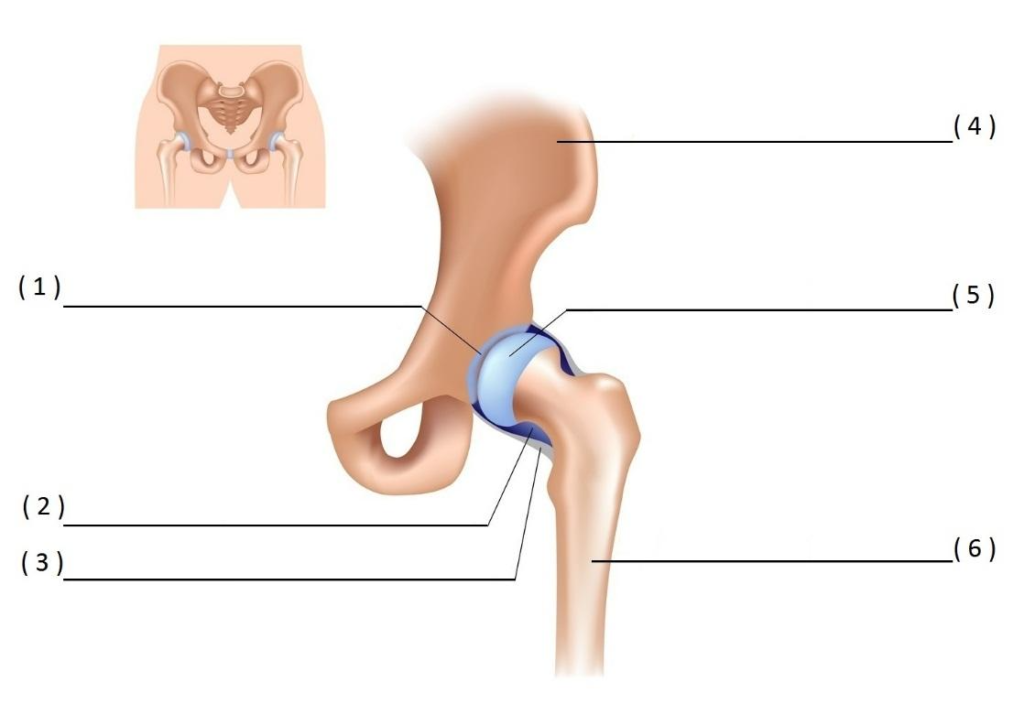
SACROILIAC JOINT

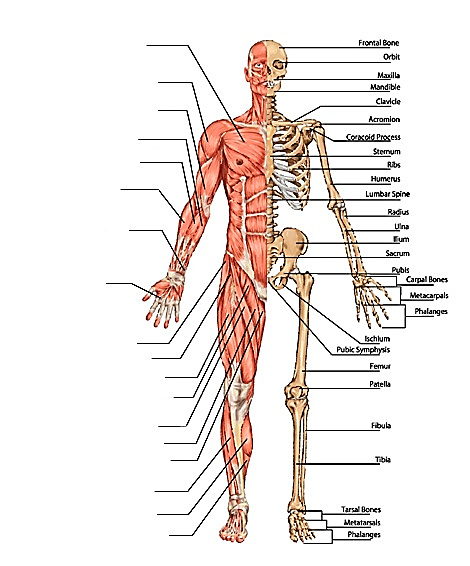
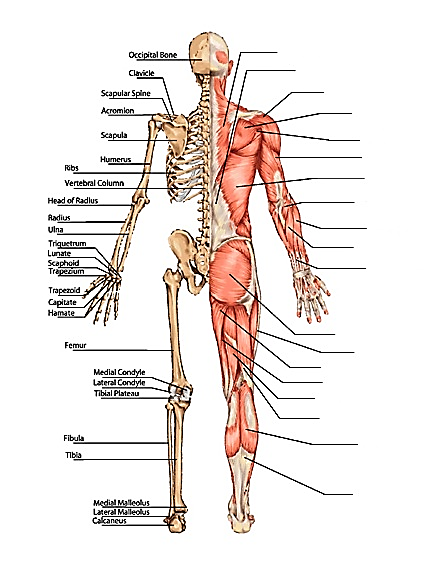
WHOLE BODY- MUSCLES & BONES
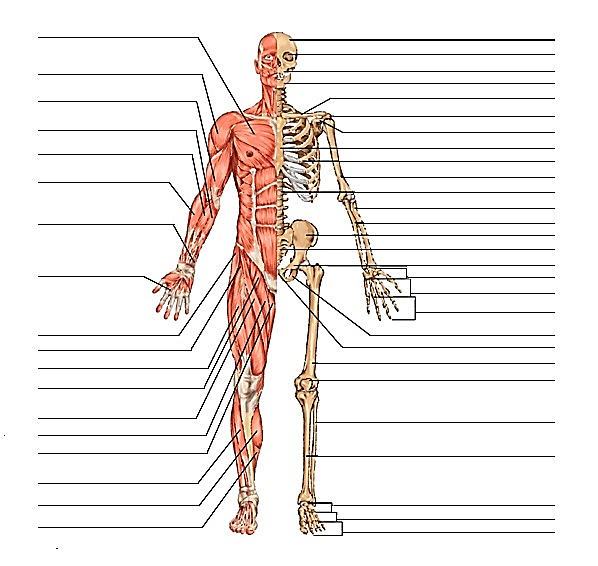
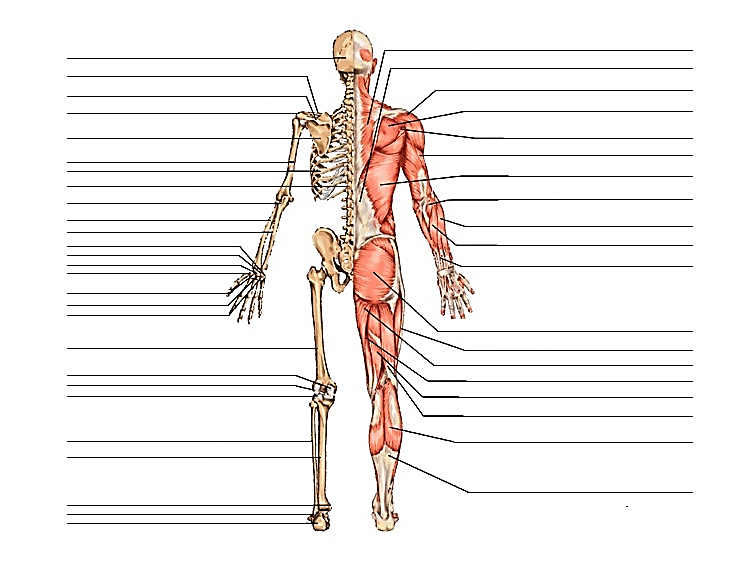
BONES
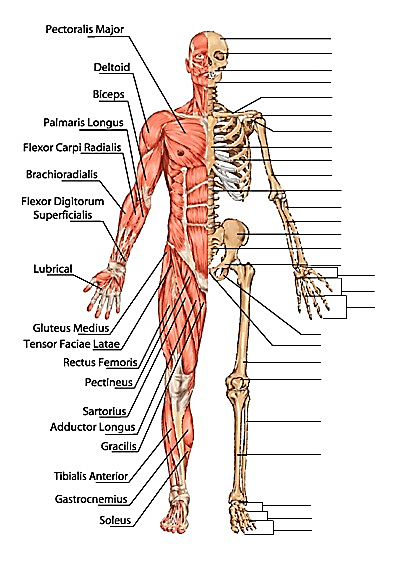

MUSCLES
Joint Movements & Mobility Quiz
- Define Range of Motion (ROM)
- Who uses ROM standards, and why?
- How are joints affected by over-stretching?
- What are the effects of diminished ROM?
- Why is joint mobility important in asana practice?
- Name and describe the movements of each of these joints.
- Ankles
- Knees
- Hips
- Spine
- Wrists
- Elbows
- Shoulders
- Scapula
- Neck
- What are the established normal ranges of motion for each joint movement?
- Ankles
- Knees
- Hips
- Spine
- Wrists
- Elbows
- Shoulders
- Neck
Muscle Pairs & Pose Examples Quiz
Part 1: For each movement type, select the key muscles involved.
- ELBOW FLEXION & EXTENSION
- SHOULDER FLEXION & EXTENSION
- SHOULDER ABDUCTION & ADDUCTION
- SHOULDER ROTATION
- SPINAL FLEXION & EXTENSION
- HIP FLEXION & EXTENSION
- HIP ABDUCTION & ADDUCTION
- HIP ROTATION
- KNEE FLEXION & EXTENSION
- ANKLE DORSIFLEXION & PLANTARFLEXION
- WRIST FLEXION & EXTENSION
- tibialis anterior & gastrocnemius + soleus
- hamstrings & quadriceps
- biceps & triceps
- rectus abdominis & erector spinae
- middle deltoid & latissimus dorsi
- wrist flexor & wrist extensor
- gluteus medius + minimus & adductors
- subscapularis + teres major & infraspinatus + teres minor
- anterior deltoid & posterior deltoid
- iliopsoas & gluteus maximus
- gluteus medius + minimus & gluteus maximus
Part 2: For each movement, name the prime mover (agonist) and antagonist muscles and provide an example of a pose or activity that uses the movement:
- Elbow flexion
- Elbow extension
- Shoulder flexion
- Shoulder extension
- Shoulder abduction
- Shoulder adduction
- Shoulder (internal) medial rotation
- Shoulder (external) lateral rotation
- Spinal flexion
- Spinal extension
- Hip flexion
- Hip extension
- Hip abduction
- Hip adduction
- Hip (internal) medial rotation
- Hip (external) lateral rotation
- Knee flexion
- Knee extension
- Ankle dorsiflexion
- Ankle plantarflexion
- Wrist flexion
- Wrist extension
Part 3: Teaching Applications
- How can teaching awareness of these muscle pairings impact students?
- Provide examples of how knowledge of the muscle relationships can inform sequencing and class planning.
Musculoskeletal System Intro Quiz
Vocabulary Mix & Match
- APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- AXIAL SKELETON
- BALL AND SOCKET JOINT
- BONES
- HINGE JOINT
- JOINT
- MUSCLE
- MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
- SYNOVIAL JOINT
- The most common type of joint in the body; freely movable
- Spine, skull and rib cage
- A type of joint that provides greater stability than other types
- The bones attached or appended to the axial skeleton (spine, skull and rib cage); bones of the upper and lower limbs plus the shoulder and pelvic girdles
- Gives humans the ability to move via bones, muscles and connective tissue
- Living tissues that form the body’s structural framework
- A band or bundle of fibrous tissue that has the ability to contract; attached to bone by tendons
- Junction / connecting point between bones
- A type of joint that allows for a wide range of movement, including rotation
Questions
- What is included in the musculoskeletal system and what does it do?
- What is a bone?
- What is meant by the axial skeleton?
- What is the appendicular skeleton?
- What is the function of bones?
- What is a joint?
- Define muscle.
- What are the three types of muscles in the body?
- What is the main function of muscles?
- Describe four additional functions of muscles.
Connective Tissue, Fascia Quiz
Vocabulary Mix & Match
- CONNECTIVE TISSUE
- FASCIA
- JOINT CAPSULE
- LIGAMENT
- MYOFASCIA
- TENDON
- A type of connective tissue that connects bones together at the joint
- A type of connective tissue that surrounds synovial joints
- A fibrous type of body tissue that connects, supports, binds, or separates other tissues or organs
- A type of connective tissue that is a sheet or band of fibrous tissue, giving contour and structure to the body
- A type of connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
- Muscles and surrounding tissues
Questions
- What is connective tissue?
- What are some examples of types of connective tissue?
- What are some functions of connective tissue?
- What is a tendon?
- What is a ligament?
- What is a joint capsule?
- Define fascia.
- Explain fascia using descriptive phrases that help students to visualize and get a clearer sense for this pervasive tissue.
- Fascia is full of sensory nerve endings that are in constant communication with the brain. What is this communication about?
- From an Energy Medicine perspective, what is a function of fascia?
- What is meant by the term “myofascia?” What is the significance of this term?
- How does the “myofascial meridian theory” differ from the traditional anatomy model?
Location & Movement Terminology Quiz
- What is flexion and extension?
- What is hyperextension?
- What is meant by lateral and medial?
- Describe adduction and abduction.
- What is meant by internal and external rotation?
- What is the meaning of anterior and posterior?
- What is meant by distal and proximal?
- What is meant in anatomy by superior and inferior?
- For what purpose related to asana has Andrey Lappa described movement differently?
- What are the three planes of motion called? What type of movement happens in each?
Muscle Movement & Contraction Quiz
Vocabulary Mix & Match
- AGONIST
- AGONIST
- ANTAGONIST
- CONCENTRIC CONTRACTION
- ECCENTRIC CONTRACTION
- FIXATOR MUSCLE
- INSERTION
- ISOMETRIC CONTRACTION
- ISOTONIC CONTRACTION
- MUSCLE CONTRACTION
- ORIGIN
- ORIGIN & INSERTION POINTS
- PRIME MOVER
- RECIPROCAL INHIBITION
- STABILIZER MUSCLE
- SYNERGIST MUSCLES
- Muscle contraction causing a slowdown of movement with gravity; muscle actively lengthens
- The muscle providing the predominant contraction for a movement
- The muscle that fixes part of the body so that movement can occur
- The activation of tension in muscle fibers
- Muscles that contract along with the prime mover to help carry out a motion
- Antagonist Relationship — When one muscle contracts, another muscle stretches
- Muscle contraction with no movement (muscle doesn’t change length); also called static contraction
- Muscle contraction causing movement against gravity; muscle actively shortens
- The places where muscles are attached to bones in relation to a movement at a joint
- An unconscious spinal reflex that causes the antagonist muscle to relax when the agonist muscle contracts
- The muscle that performs motion in the opposite direction of the agonist; it stretches passively
- The distal (away) attachment of muscle to bone; on the bone that is most generally moved
- Muscle contraction with movement
- Another name for stabilizer
- The proximal (near) attachment of muscle to bone; on the bone that is relatively stationary
- Another name for agonist muscle
Questions
- What is the purpose of muscle?
- How does movement happen?
- What is muscle cramping? Why might a muscle cramp?
- What might help with muscle cramping?
- What is muscle contraction?
- How do origin and insertion points relate to muscle contraction?
- What are three types of muscle contraction and an example for each?
- What is meant by the agonist and antagonist relationship? What is an example?
- What is reciprocal inhibition and how can you use this knowledge in practice?
Hyperextension & Hypermobility Quiz 1.2
- Describe a healthy musculoskeletal system and the effects of optimally functioning joints.
- List potential issues related to musculoskeletal health.
- Describe potential consequences of diminished mobility.
- Describe potential consequences of excessive mobility.
- Discuss how hypermobility may be misunderstood as “being good at yoga.”
- Describe the ways in which yoga practice is a powerful tool for optimizing musculoskeletal balance.
- Comment on using asana to move joints through their healthy range of motion.
- Provide general considerations to keep in mind to optimize joint health.
- Provide general asana practice techniques that can help to optimize joint health with all students.
- Describe hyperextension.
- Provide examples of addressing hyperextension.
- Define joint hypermobility and discuss considerations regarding the number of hypermobile joints a person has.
- Describe the felt sense of being in a hypermobile body.
- Discuss teaching considerations and techniques for students with hypermobile joints.
- Describe ways to teach students with hypermobility how to stretch in ways to avoid excessive joint movement.
Spinal Regions & Vertebrae Quiz
Vocabulary Mix & Match
- BACKBONE
- CERVICAL SPINE
- COCCYX
- LUMBAR SPINE
- NORMAL CURVES
- SACRUM
- SPINAL COLUMN
- SPINE
- SPINOUS PROCESSES
- THORACIC SPINE
- VERTEBRAE
- VERTEBRAL COLUMN
- Another name for the spine
- A term used by anatomists to underscore the importance of the four spinal curves
- Another name for the spine
- Plural of “vertebra,” specialized bones that make up the spine
- Five fused vertebrae that make up the base of the spine and the back of the pelvis
- Another name for the spine
- Top region of the spine, labeled C1-C7
- Low back region of the spine, labeled L1-L5
- Made up of 33 specialized bones called vertebrae, houses the spinal cord which provides communication between brain and body
- Middle region of the spine, labeled T1-T12
- Three to five fused vertebrae with a tip that typically points straight down
- The bony projections from the vertebra that you can feel when you palpate your spine; they provide attachment points for muscles and ligaments
Questions
- What are some other names for the spine?
- What regions make up the spinal column? How many vertebrae are in each region? Which are fused?
- How are vertebrae labeled/numbered?
- Where do we experience the most movement in the spine, and why?
- What is the shape of each curve?
- What is the sacrum?
- What are the “primary curves” and why are they given that name?
- What are the “secondary curves” and why are they given that name?
- How can Savasana be used to identify spinal curves?
- What are vertebrae?
- Describe the general structure of an individual vertebra.
- What are intervertebral discs?
Back Muscles Quiz
- Describe two ways that back muscles may be categorized.
- List the muscles in each category and their primary association.
- Where are superficial back muscles located? What actions are associated with them, and what asanas strengthen and stretch them?
- Where are intermediate back muscles located? What do they do, and what asanas stretch and strengthen them?
- Where are the deep back muscles located? What actions are they responsible for?
- What is the relationship between deep back muscles and the core?
- Describe the erector spinae and their functions.
- Provide asana examples for strengthening and stretching the erector spinae.
- Describe the quadratus lumborum (QL) and its functions.
- Discuss potential issues with the QL and a type of strengthening that can help support it.
- What do multifidus muscles do and how can knowledge of them help students?
Spinal Functions Quiz
- What are the functions of the spine?
- In what two complementary ways is the spine designed to function?
- Explain how the curves of the spine work.
- What are the attributes of a healthy spine?
- What is the function of the spinal cord? Provide a metaphor to describe it.
- Give examples of areas of the body supplied by the nerves in the spine, and potential conditions associated with nervous system issues.
Spinal Movements Quiz
- What are the six directions of spinal movement?
- What two additional types of spinal movement are we concerned with in yoga?
- Give an asana example for each of the types of spinal movement.
- What is the objective of spinal / axial extension poses?
- What is compression and when is it usually desirable?
- What are some teaching considerations related to spinal alignment in forward bends?
- What are some teaching considerations related to spinal alignment in backbends?
- What are some teaching considerations related to spinal alignment in lateral bends?
- What are some teaching considerations related to spinal alignment in twists?
- What are some teaching considerations related to spinal extension?
- What are some teaching considerations related to spinal alignment in inversions?
Healthy Posture Quiz
Vocabulary Mix & Match
- MUSCLE MEMORY
- POSTURE
- ANATOMICAL POSITION
- HEALTHY POSTURE
- STANDING IN NEUTRAL
- NEUTRAL SPINE
- STANDARD ANATOMICAL POSITION
- ISCHEMIA
- SENSORY MOTOR AMNESIA
- NEUTRAL PELVIS
- Movement or posture that has become automatic; a result of the nervous system shifting control and memory of a repeated pattern from areas of the brain responsible for making voluntary decisions to making them subconscious
- A collection of (typically unconscious) habits and holding patterns (which form our muscle memory) that create “an attitude of the body” or an “orientation to the present moment” which reinforces itself through bodily structures and physiology
- In humans, defined as “standing up straight with the body at rest”
- A natural bearing of the body that includes a comfortably neutral spine and promotes healthy internal functioning and muscular efficiency
- Another way to describe anatomical position; refers to standing with the bones stacked vertically and the two sides of the body displaying symmetry
- A state in which the spinal curves are not too much or too little for the individual’s healthy norm
- Standing up straight and facing forward with the arms by the sides and palms facing forward
- Insufficient supply of blood to an organ; As it relates to posture, refers to the compression of blood vessels resulting from chronic muscular tension, causing pain and damage
- The natural way in which bodily movement and posture becomes “automatic and involuntary” leading to loss of sensation, a lack of awareness of the muscular pattern, and a temporary inability to relax tight muscles
- A state of equal hip height, a neutral pelvic tilt, a neutral front-to-back placement and the pelvis is pointing straight ahead
Questions
- Define posture.
- Discuss how posture manifests.
- Is posture genetic?
- What criteria are often used when identifying healthy posture?
- Why does healthy posture matter?
- Describe a “neutral” spine.
- Why may students find it difficult to identify a neutral spine?
- Describe four considerations for pelvic alignment in Tadasana (Mountain Pose).
- While general symmetry is correlated with healthy posture, describe Jenni Rawlings case for focusing less on symmetry and more on balance.
- What common lifestyle factor has a significant impact on posture and, therefore, healthy functioning?
- Discuss the maintenance of healthy posture.
Postural Issues & Conditions Quiz
Vocabulary Mix & Match
- HYPERKYPHOSIS
- HYPERLORDOSIS
- KYPHOSIS
- LORDOSIS
- LOWER CROSSED SYNDROME
- SWAYBACK / HOLLOW BACK / SADDLE BACK
- THORACIC KYPHOSIS
- UPPER CROSSED SYNDROME
- Other names for hyperlordosis
- Excessive forward curvature of the thoracic spine (clinically defined as greater than 50 degrees)
- A postural pattern in which muscles around the shoulder girdle are out of balance; may appear as rounded shoulders and upper back, winging shoulder blades and a forward head
- Another name for kyphosis
- Sometimes used for hyperlordosis
- Excessive inward curvature of the lumbar spine, causing a forward (anterior) pelvic tilt
- Another name for kyphosis
- A postural pattern in which muscles of the core, back and legs are out of balance; may present as posterior pelvic crossed syndrome or anterior pelvic crossed syndrome
Questions
- Name 15 issues related to the spine that various students might exhibit.
- For what functional reason does the thoracic spine have limited mobility?
- What are potential consequences of lack of healthy mobility in the thoracic spine?
- What are potential causes of hyperlordosis?
- What is kyphosis? Describe potential symptoms.
- What are potential causes of kyphosis?
- What is scoliosis?
- What is the difference between structural scoliosis and functional scoliosis?
Spine & Posture Considerations Quiz
- What are two primary objectives of asana that relate to the spine?
- What is compensation as it relates to spinal curves and why is it important?
- What three foundational teachings related to the spine might you consider conveying to your students?
- How might you teach students to feel their natural spinal curves?
- Describe a simple exercise for students to learn more about their particular body and potential compensation patterns.
- What are two common compensation-related issues?
- What teachings can help students to address common compensation-related issues?
Core Form & Function Quiz
Vocabulary Mix & Match
- CORE MUSCLES
- ERECTOR SPINAE (SPINAL ERECTORS)
- MULTIFIDUS MUSCLES
- SUPERFICIAL ABDOMINALS
- TRANSVERSUS ABDOMINIS (TA)
- A series of deep muscles that run the length of the spine, stabilizing vertebrae and assisting in spinal rotation and extension
- Rectus abdominis, internal obliques and external obliques
- Muscles that stabilize the spine and pelvis
- Deep core muscle that wraps around torso and supports spine
- Three groups of muscles that run the length of either side of the spine, helping to maintain erect posture
Questions
- What comprises the core?
- Describe four functions of the core.
- List components of the core.
- What does the rectus abdominis do? Gives example of asanas that strengthen and stretch it.
- What do the obliques do? Provide an example of asana that work them.
- What does the TA do? What is an example of an asana that works it?
- What are deep back muscles and how do the relate to the core?
- Define and discuss the significance of intra-abdominal pressure (IAP).
- What simple exercise can give students the experience of feeling the abdominal muscles in their role as stabilizers?
Core Fundamental Teachings Quiz
- Summarize some teachings that are valuable in helping students to optimize their core health?
- How can you help students gain inner awareness of their core musculature?
- Describe the potential adverse effects of excessive tightness in the core.
- What is meant by stabilizers and prime movers? Why is this important when choosing core strengthening exercises?
- A key factor in sustained core health is bringing awareness to movement patterns. Expand on this teaching.
- What are some considerations that can help to inform your choice of practices and teachings related to core health?
- What is the anatomical meaning of abdomen?
- Describe ways to effectively use verbiage such as “abdomen,” “belly,” and “core” in teaching.
TA & Engaging Deeper Abs Quiz
- Describe the transversus abdominis (TA) and its location.
- Describe functions of the TA.
- What is the effect from engaging / contracting the TA?
- How can identifying the sensation of contracting deeper abdominals benefit students? Provide information to support this learning process.
- Describe simple exercises that can help students to identify the TA.
- When performing a lower abdominal exercise such as a leg lift, what clue can indicate the deeper abdominals are not engaged?
The Pelvic Floor Quiz
- Describe the pelvic floor. Provide a visual and remark on its function and sensitivities.
- Where is the pelvic floor located?
- What defines healthy, natural movement of the pelvic floor?
- Describe three general functions of the pelvic floor.
- How do pelvic floor muscles contribute to core functioning?
- What are some potential issues associated with the pelvic floor?
- What factors may lead to pelvic floor weakness?
- What factors may lead to a tight pelvic floor?
- What other habits, practices and factors may cause pelvic floor issues?
- What teachings and practices may contribute to pelvic floor health?
